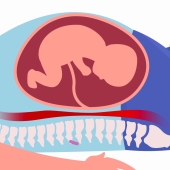
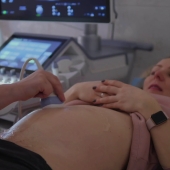
Ultrasound examinations can be performed on most parts of the body and provide excellent information about a variety of conditions – from pregnancy to gall stones, varicose veins and even muscle tears.
During an Ultrasound examination, sound waves are bounced back from parts of the body (like sonar) to give black and white (or in some cases now, colour) images.
Ultrasound is particularly useful in pregnancy as there are no known harmful effects from its diagnostic use. Modern Ultrasound equipment shows detail in “real‐time”, not as still images. This enables a moving image to be seen on the screen.
These examinations are carried out and interpreted by a Radiologist (a Doctor trained in reading X‐rays and Ultrasounds) and a Sonographer (a Technologist trained in Ultrasound imaging).
The Sonographer uses a transducer (a hand‐held device which produces and receives the sound waves) to display the images. The Ultrasound procedure is usually painless.
Most Common Scans:
- Early Pregnancy (Before 12 weeks)
- Assist with dating
- Early check of general pregnancy health
- Nuchal Translucency Assessment
- Assesses for chromosomal abnormalities
- Performed in conjunction with blood test
- Morphology Scan (18-20 weeks)
- Third Trimester Scan
- 279 views