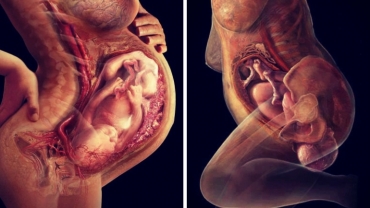
Vacuum-assisted vaginal delivery or vacuum extraction, is a method to assist delivery of a baby using a vacuum device. It is used in the second stage of labour if it has not progressed adequately. It may be an alternative to a forceps delivery and caesarean section. It cannot be used when the baby is in the breech position or for premature births. The use of VE is generally safe, but it can occasionally have negative effects on either the mother or the child.
The woman is placed in the lithotomy position and assists throughout the process by pushing. A suction cup is placed onto the head of the baby and the suction draws the skin from the scalp into the cup. Correct placement of the cup directly over the flexion point, about 3 cm anterior from the occipital (posterior) fontanelle, is critical to the success of a VE. Ventouse devices have handles to allow for traction. When the baby's head is delivered, the device is detached, allowing the birthing attendant and the mother to complete the delivery of the baby.
For proper use of the ventouse, the maternal cervix has to be fully dilated, the head engaged in the birth canal, and the head position known. If the ventouse attempt fails, it may be necessary to deliver the infant by forceps or caesarean section.
- 6721 views