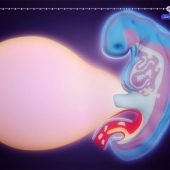
An Intrauterine insemination (IUI) is a procedure done to help a woman get pregnant. The goal of IUI is to increase the number of sperm that reach the fallopian tubes and subsequently increase the chance of fertilization. An intrauterine insemination must be performed just before or right after a woman ovulates, so that an egg is available for fertilisation.
During the procedure, a speculum will be inserted into the vagina, so that the doctor can see the cervix. A syringe is loaded with a small amount of fluid containing the washed sperm. Then the syringe will be attached to a long thin tube called the catheter. The doctor will insert the catheter into the vagina; the tip of the catheter will be guided through the opening in the cervix and into the uterus. Once the catheter is inside the uterus, the doctor will inject the sperm.
IUI may be selected as a fertility treatment for any of the following conditions as well:
- Unexplained infertility
- A hostile cervical condition, including cervical mucus problems
- Cervical scar tissue from past procedures which may hinder the sperms’ ability to enter the uterus
- Ejaculation dysfunction
IUI is not recommended for the following patients:
- Women who have severe disease of the fallopian tubes
- Women with a history of pelvic infections
- Women with moderate to severe endometriosis
- 1684 views