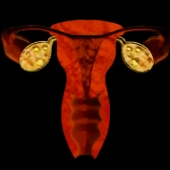
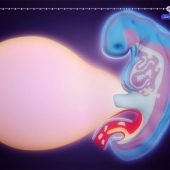
In a normal menstrual cycle, women experience menstruation (also known as a period) followed by the release of an egg. During menstruation blood, cells and mucus are discharged from the uterus.
The menstrual cycle starts on the first day of the menstrual period (referred to as day one) and ends the day before the next period begins. While the length of the menstrual cycle is often 28 days, it can vary between women and from one cycle to the next. It is common for women to experience cycles that last anywhere from 20 to 40 days. Cycles longer than six weeks are considered unusual.
Ovulation occurs about 14-16 days before women have their period (not 14 days after the start of their period). The second half of the cycle, ovulation to menstruation, is fairly consistently the same length, but the first part changes from person to person and from cycle to cycle. In rare cases, a women may ovulate twice in a month, once from each ovary.
Conception/Fertilization of an egg, can only occur after ovulation. The egg stays alive for about 24 hours once released from the ovary. Sperm can stay alive inside a woman's body for 3-4 days, but possibly as long as 6-7 days. If a couple has intercourse before or after ovulation occurs, they can get pregnant, since the live sperm are already inside the woman's body when ovulation occurs. Thus a woman can become pregnant from intercourse for about 7-10 days in the middle of her cycle.
- 2148 views